7. Application Layerserve
as application interfaces with network functionality, manage how
applications can access the network and then generate an error message.
TCP / IP application layer is the Application. Application Layer has 8 protocol, namely:DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocol): for IP distribution with a limited number of IP numbersDNS (domain name server): Database engine domain name and IP numbersFTP (File Transfer Protocol): A protocol for file transferHTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol): A protocol to transfer HTML files and WebMIME (Multipurpose Internet mail extensions): protocol for sending binary files in text formNNTP (network news transfer protocol): protocol for receiving and sending news groupPOP (Post Office Protocol): A protocol to retrieve mail from the serverSMB (Server messages block): protocol for the transfer of DOS and Windows file servers
6 Presentation Layerserves to translate the data to be in tranmisikan by the application into a format that can be ditranmiskan through the network.
TCP / IP alpikasi, is the presentation layer. Presentation Layer 4 protocol that have:SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol): protocol for the exchange of mailSNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): A protocol for network managementTelnet: A protocol for remote accessTFTP (Trivial FTP): A protocol for file transfer
5 Session Layerserves to define how connections can be made maintained or destroyed.
TCP / IP alpikasi, Layer is session. Session Layer 3 protocol has:NETBIOS (Network basic input output system): BIOS standard networkRPC (remote procedure call): remote procedure callsSOCKET: Input outpu for BSD-UNIX network types
4 Transport Layerserves to break down the data into ppaket-data packets and provide the serial number for the packages that can be rearranged to the destination as it arrives.
TCP / IP Transport, Transport Layer is. Transport Layer 2 protocol has:TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A protocol-oriented data exchange (conection oriented)UDP (user datagram protocol): Protocol data exchange non-orientation (Connectionless)
3 Network Layerserves to identify the IP addresses making headers for the packets and then routing through the internet router and switc working USING layer-3.
TCP / IP Network Layer is the Internet. Network Layer 4 protocol has:IP (Internet Protocol): A protocol for routing settle itRIP (Routing Information Protocol): Protocol to select the routingARP (address resolution protocol): Protocol to get the information right from the hardware IP numbersRARP (Reserve ARP): protocol to obtain the IP address of the hardware
2 Data Link Layerfunction to determine how the data bits are organized into a format called a Frame
TCP / IP Data Link, Network Interface Layer is. Data Link Layer is divided into two, namely:Data Link LLC PPP (Point to Point Protocol): A protocol for point to pointData Link MAC SLIP (Serial line internet protocol): Protocol by using a serial connection
1 Physical Layerserves to mendefinisakan network transmission media, signaling method, bit synchronization, network architecture, (such as ethernet or TokenRing), network topology and wiring.
TCP / IP Physical Layer with Data Link. Protocol for Physical Layer:Ethernet, FDDI, ISDN, ATM

TCP / IP application layer is the Application. Application Layer has 8 protocol, namely:DHCP (Dynamic host configuration protocol): for IP distribution with a limited number of IP numbersDNS (domain name server): Database engine domain name and IP numbersFTP (File Transfer Protocol): A protocol for file transferHTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol): A protocol to transfer HTML files and WebMIME (Multipurpose Internet mail extensions): protocol for sending binary files in text formNNTP (network news transfer protocol): protocol for receiving and sending news groupPOP (Post Office Protocol): A protocol to retrieve mail from the serverSMB (Server messages block): protocol for the transfer of DOS and Windows file servers
6 Presentation Layerserves to translate the data to be in tranmisikan by the application into a format that can be ditranmiskan through the network.
TCP / IP alpikasi, is the presentation layer. Presentation Layer 4 protocol that have:SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol): protocol for the exchange of mailSNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): A protocol for network managementTelnet: A protocol for remote accessTFTP (Trivial FTP): A protocol for file transfer
5 Session Layerserves to define how connections can be made maintained or destroyed.
TCP / IP alpikasi, Layer is session. Session Layer 3 protocol has:NETBIOS (Network basic input output system): BIOS standard networkRPC (remote procedure call): remote procedure callsSOCKET: Input outpu for BSD-UNIX network types
4 Transport Layerserves to break down the data into ppaket-data packets and provide the serial number for the packages that can be rearranged to the destination as it arrives.
TCP / IP Transport, Transport Layer is. Transport Layer 2 protocol has:TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): A protocol-oriented data exchange (conection oriented)UDP (user datagram protocol): Protocol data exchange non-orientation (Connectionless)
3 Network Layerserves to identify the IP addresses making headers for the packets and then routing through the internet router and switc working USING layer-3.
TCP / IP Network Layer is the Internet. Network Layer 4 protocol has:IP (Internet Protocol): A protocol for routing settle itRIP (Routing Information Protocol): Protocol to select the routingARP (address resolution protocol): Protocol to get the information right from the hardware IP numbersRARP (Reserve ARP): protocol to obtain the IP address of the hardware
2 Data Link Layerfunction to determine how the data bits are organized into a format called a Frame
TCP / IP Data Link, Network Interface Layer is. Data Link Layer is divided into two, namely:Data Link LLC PPP (Point to Point Protocol): A protocol for point to pointData Link MAC SLIP (Serial line internet protocol): Protocol by using a serial connection
1 Physical Layerserves to mendefinisakan network transmission media, signaling method, bit synchronization, network architecture, (such as ethernet or TokenRing), network topology and wiring.
TCP / IP Physical Layer with Data Link. Protocol for Physical Layer:Ethernet, FDDI, ISDN, ATM





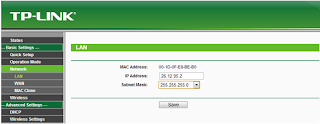
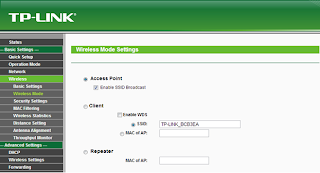
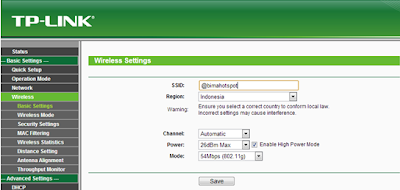



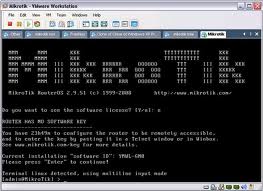











.jpg)